4. DNS Components
DNS service has 3 components:
The first is a “Name Space” that establishes the syntactical rules for creating and structuring legal DNS names.
The second is a Globally Distributed Database implemented on a network of “Name Servers”.
The third is "Resolver" software,understands how to formulate a DNS query and is built into all Internet-capable application.
- DNS Resolver
A DNS resolver (DNS lookup tool), resolves an individual host name to an IP address
- DNS Resolver Cache
A temporary database, maintained by a computer's OS, that contains records of all the recent visits and attempted visits to websites and other Internet domains.
No network traffic is generated to resolve the queries of sites present in cache.
Routers and ISP (Internet Service Providers) also have DNS cache.This speedup the process of DNS lookup.
View DNS cache on Windows
Type following command in CMD
ipconfig /displaydns
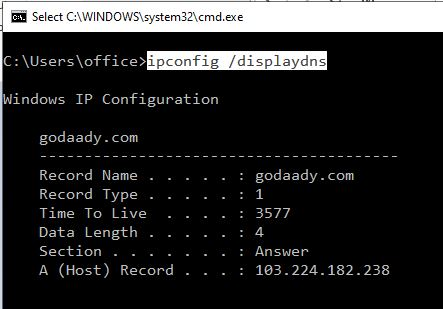
The "A" record is the portion of the DNS entry that contains the IP address for the given host name.
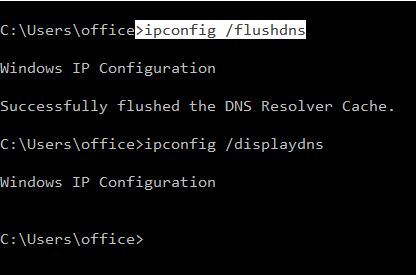
Clear DNS cache on Windows
ipconfig /flushdns
Tip: Rebooting a router clears the DNS entries stored in its temporary memory.
- Name servers (NS)
They contain the database of names and IP addresses and serves DNS requests for clients.Each zone has a primary or master name server, which is the authoritative source for the zone's resource records.
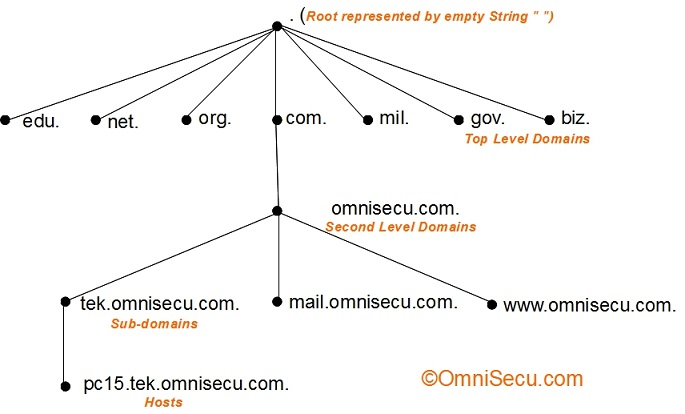
- Name space
The entire collection of DNS administrative domains throughout the world are organized in a hierarchy called the DNS namespace.
The DNS namespace tree has a unique root and large number of sub-trees. A domain is a subtree of the DNS name space.